This put up could include affiliate hyperlinks. Please learn our disclosure.
(Managing Daybreak Phenomenon with Basal Insulin is excerpted from Suppose Like A Pancreas: A Sensible Information to Managing Diabetes With Insulin by Gary Scheiner MS, CDE, DaCapo Press, 2011)
The liver is a captivating organ. It does a couple of hundred various things. One in all its major capabilities is to retailer glucose (in a dense, compact kind referred to as “glycogen”) and secrete it steadily into the bloodstream with the intention to present our physique’s very important organs and tissues with a continuing supply of gas.
That is what retains your coronary heart beating, mind pondering, lungs respiration, and digestive system, uh, digesting, just about on a regular basis.
With the intention to switch the liver’s regular provide of glucose into the physique’s cells, the pancreas usually secretes a small quantity of insulin into the bloodstream each couple of minutes. That is referred to as basal insulin.
Not solely does basal insulin guarantee a gentle power supply for the physique’s cells, it additionally retains the liver from dumping out an excessive amount of glucose unexpectedly. Too little basal insulin, or a whole lack of insulin, would lead to a pointy rise in blood sugar ranges.
So, you would possibly say that basal insulin and the liver are in “equilibrium” with one another. The basal insulin ought to match the liver’s secretion of glucose all through the day and night time.
Within the absence of meals, train, and rapid-acting/mealtime insulin, the basal insulin ought to maintain the blood sugar stage good and regular.
Every particular person’s basal insulin requirement is exclusive. Sometimes, basal insulin wants are highest in the course of the night time and early morning, and lowest in the course of the day. That is as a result of manufacturing of blood sugar–elevating hormones in the course of the night time, and enhanced sensitivity to insulin that comes with daytime bodily exercise. Two hormones specifically – cortisol and progress hormone – trigger the liver’s pure ebb and stream in glucose secretion.
Throughout an individual’s progress years (previous to age 21), basal insulin wants are usually comparatively excessive all through the night time, drop by means of the morning hours, and steadily improve from midday to midnight. Most adults (age 21+) exhibit an abrupt improve in basal insulin necessities in the course of the early morning hours, adopted by a drop-off till noontime, a low/flat stage within the afternoon, and a gradual improve within the night. This peak in basal insulin in the course of the early morning hours is usually known as a daybreak phenomenon.
Basal insulin may be provided in quite a lot of methods. Intermediate-acting insulin (NPH) taken as soon as each day will often present background insulin across the clock, albeit at a lot greater ranges 4 to eight hours after injection and at a lot decrease ranges at 16 to 24 hours. Lengthy-acting basal insulins (glargine and detemir) supply comparatively peakless insulin ranges for about 24 hours. Insulin pumps ship rapid-acting insulin in small pulses all through the day and night time. With a pump, the basal insulin stage may be adjusted and fine-tuned to match the physique’s ebb and stream in basal insulin wants. It’s also doable to mix varied types of long-acting insulin to simulate the physique’s regular basal insulin secretion.
The next figures illustrate the motion profiles of varied kinds of basal insulin packages.
Basal insulin provided by NPH at bedtime
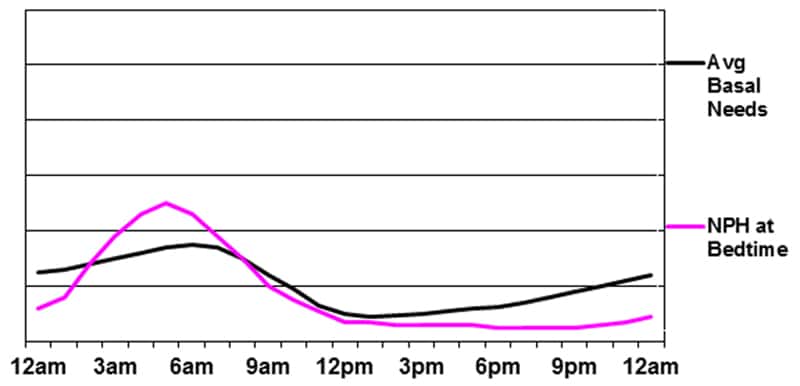
The primary benefit of this program is the height that happens in the course of the pre-dawn hours. The disadvantages embody the unpredictability of the height (as a consequence of NPH’s diversified fee of absorption from day after day), the potential for low glucose within the early morning (as a result of important peak in the course of the night time) and the probability that that late afternoon/night blood sugar will rise because the NPH tapers off.
Basal insulin provided by NPH within the morning and night
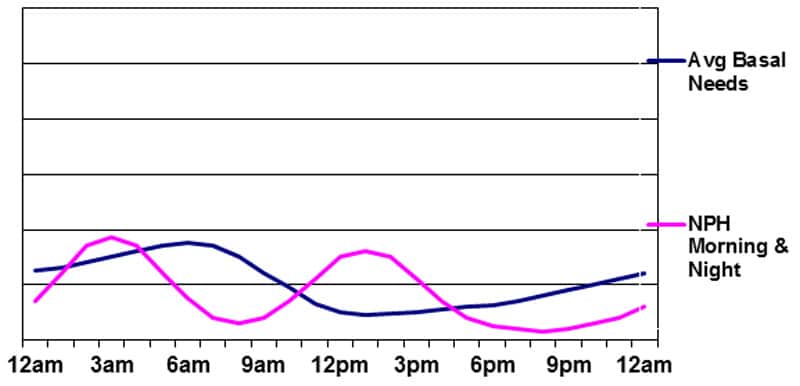
Some great benefits of this program are the height in basal insulin in the course of the night time and the opportunity of utilizing the morning NPH peak to cowl the carbs eaten at lunchtime. The drawbacks are the identical as these in Determine 3 above, plus the foremost problem of getting to adapt to a inflexible meal/snack schedule in the course of the day as a result of peak of the morning NPH insulin. Because the graphic clearly reveals, the sort of basal insulin program does a poor job of matching the physique’s wants. It not often produces steady glucose ranges – notably in the course of the daytime.
Sadly, those that use “premixed” insulin twice each day are, primarily, using this strategy for his or her basal program. Every injection of premixed insulin comprises wherever from 50-75% NPH insulin, with the rest being both Common or rapid-acting insulin.
Basal insulin provided by glargine (Lantus) or detemir (Levemir)
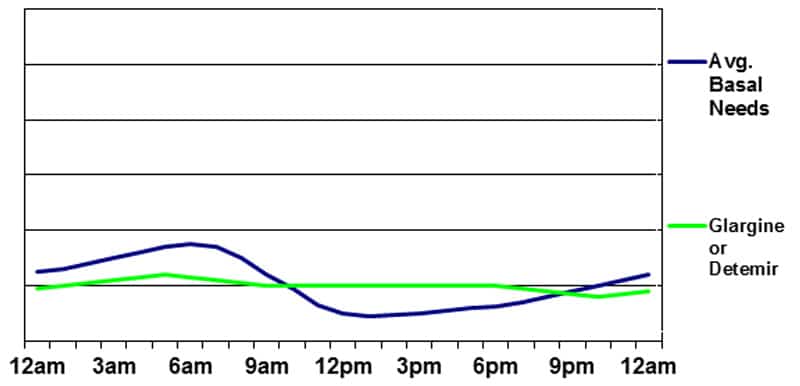
Glargine (Lantus) is often taken as soon as each day, however generally is taken twice – notably when low doses are getting used. Detemir (Levemir) is often taken twice each day, however often may be taken as soon as a day. When basal insulin is injected twice each day, it’s affordable to separate the doses evenly and take them roughly 12 hours aside. Taking extra within the night and fewer within the morning doesn’t often produce a desired “peak” at any specific time. When taken as soon as each day, it’s often finest to take the injection within the morning on a constant 24-hour cycle. Analysis has proven that the morning injection has the least potential to trigger an undesired blood sugar rise when the insulin is truly fizzling out at round 20-24 hours.
The primary benefit of utilizing glargine or detemir is the comparatively unwavering stream of insulin (a really slight peak could happen 6 to 10 hours after injection of detemir) and constant absorption sample. The disadvantages embody the potential for a gradual blood sugar rise in the course of the night time (as a result of lack of a pre-dawn peak) and across the time of the injection when the insulin is taken as soon as each day (the basal insulin could “put on off” a couple of hours early and take a couple of hours to “kick in”). There may be additionally potential for a gradual blood sugar drop within the afternoon because the basal insulin stage could exceed the liver’s manufacturing of glucose.
Basal insulin provided by Glargine or Detemir plus Night NPH
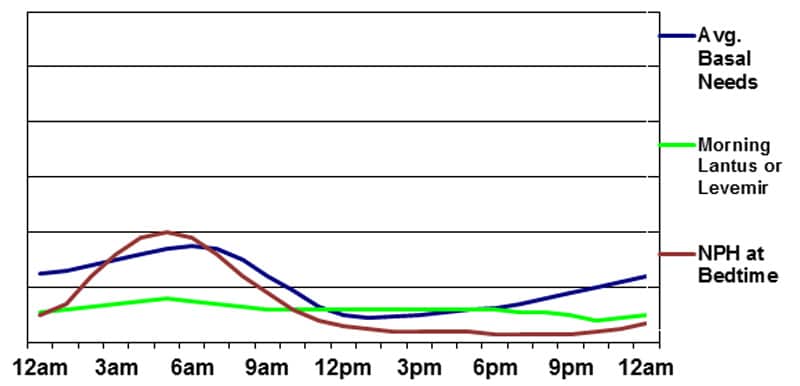
With the intention to overcome among the potential issues created through the use of solely basal or NPH insulin to satisfy the physique’s basal wants, it’s doable to mix the 2. When NPH is added at nighttime, glargine or detemir may be taken as soon as each day at a decrease dose than if used with out NPH. This minimizes the chance of getting glucose ranges drop between meals in the course of the day. By including a modest night or bedtime dose of NPH, a nighttime/early-morning peak may be achieved. This program presents the distinctive benefit of permitting day-to-day adjustment of the in a single day basal insulin stage by making minute modifications to the NPH dose with out affecting the basal insulin stage the next day.
The disadvantages embody the necessity for at the very least two separate injections and the filling of a number of prescriptions. There may be additionally potential for mixing up doses or taking the flawed insulin on the flawed time since a number of several types of insulin are being utilized concurrently.
Basal insulin provided by Insulin Pump Remedy
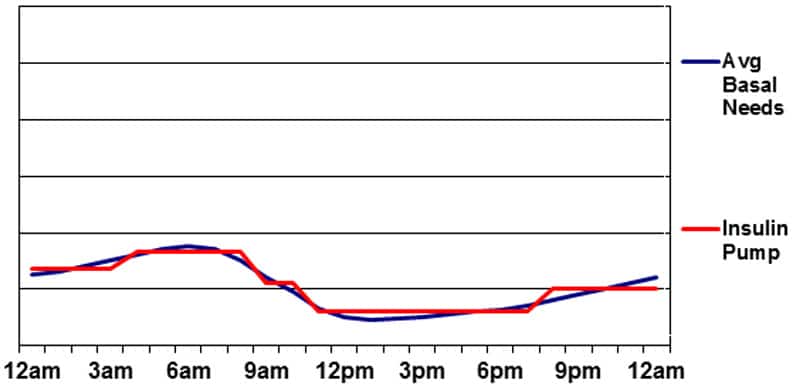
Pump remedy presents the best diploma of maneuverability when it comes to matching basal insulin to the physique’s wants. As a result of small pulses of rapid-acting insulin are used to ship basal insulin, variations in peak or motion time will not be a problem. Modifications may be made to the basal insulin supply on the hour or half-hour, so “peaks and valleys” can simply be constructed into this system. Pumps additionally allow momentary modifications to basal insulin ranges with the intention to accommodate short-term modifications in basal insulin wants (for conditions corresponding to sickness, excessive/low exercise ranges, and stress).
Maybe the best disadvantage to delivering basal insulin with a pump is the chance of ketoacidosis. Any mechanical drawback leading to an absence of basal insulin supply can lead to a extreme insulin deficiency in just some hours. With none insulin within the bloodstream, the physique’s cells start burning giant quantities of fats (as an alternative of sugar) for power. The result’s the manufacturing of acidic ketone molecules—a pure waste product of fats metabolism. This not often happens when taking injections of long-acting insulin since there may be nearly at all times some insulin working so long as injections will not be missed.
Profitable pump use would require satisfactory follow-up and fine-tuning. This could embody:
- Basal fee testing all through the day and night time (fasting for 8- to 10-hour intervals and testing blood sugars to see if they’re holding regular)
- Advantageous-tuning of bolus formulation (based mostly on record-keeping)
- Troubleshooting and prevention of emergencies corresponding to DKA (diabetic ketoacidosis); and
- Use of superior pump options corresponding to prolonged boluses and momentary basal charges.












